In 2024, 13.5% of enterprises in the EU with 10 or more employees used artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to conduct their business, indicating a 5.5 percentage points (pp) growth from 8.0% in 2023.
The highest shares of these enterprises were in Denmark (27.6%), Sweden (25.1%) and Belgium (24.7%). At the other end were Romania (3.1%), Poland (5.9%) and Bulgaria (6.5%).
All EU countries recorded increases in the share of enterprises using AI technologies compared with 2023, with Sweden experiencing the highest increase of 14.7 pp, followed by Denmark (+12.4 pp) and Belgium (+10.9 pp). By contrast, modest increases were recorded in Portugal (+0.8 pp), Romania (+1.6 pp) and Spain (+2.1 pp) – Source dataset: isoc_eb_ai.

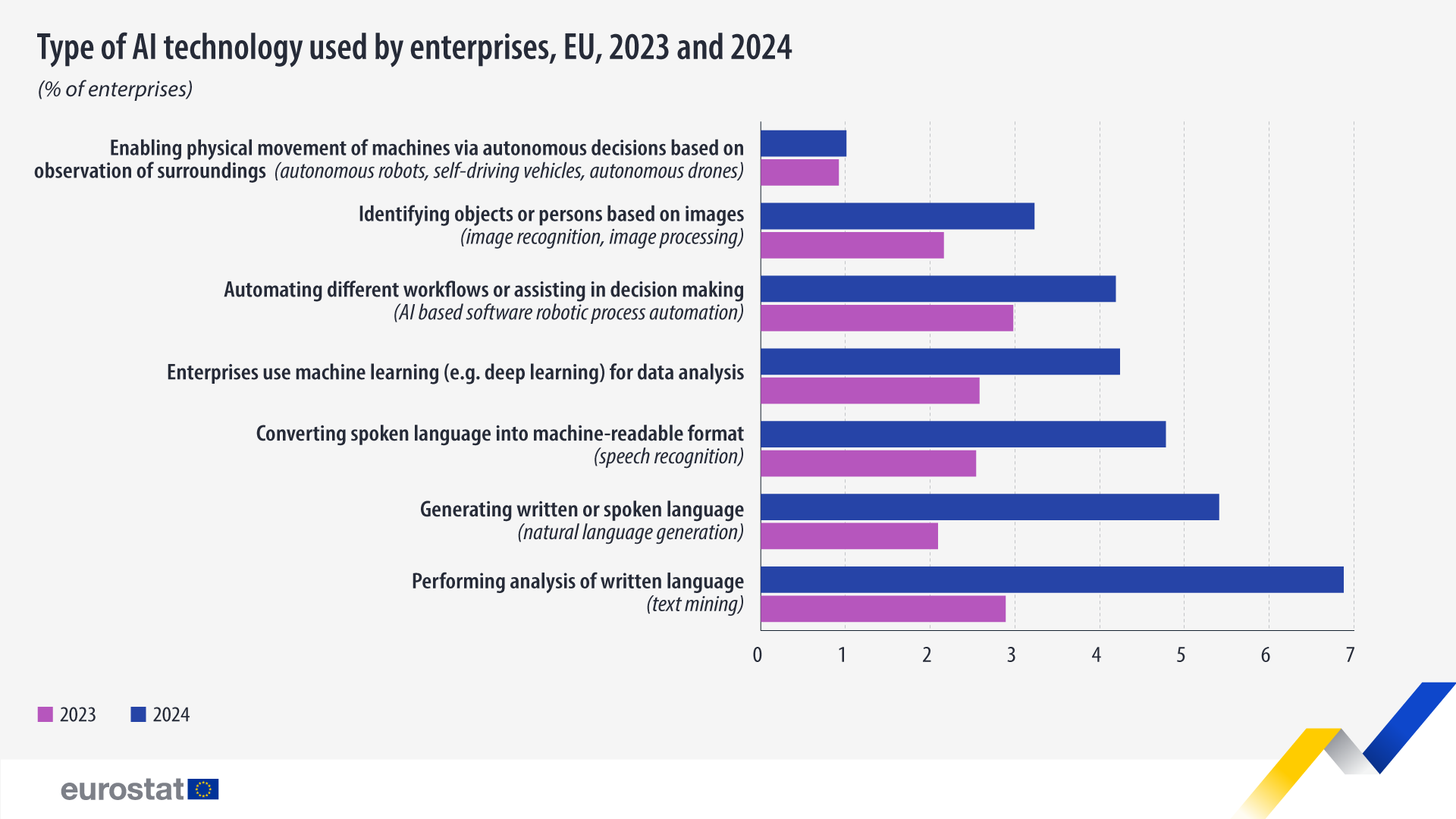
Enterprises continued to adopt various AI technologies to enhance their operations. The most used AI technology was performing analysis of written language (text mining). It was adopted by 6.9% of enterprises after following a 4.0 pp year-on-year increase. The second most used AI technology was generating written or spoken language (natural language generation), used by 5.4% of enterprises (+3.3 pp compared with 2023). This was followed by converting spoken language into machine-readable format (speech recognition), used by 4.8% enterprises (+2.2 pp) – Source dataset: isoc_eb_ai.
More information
- Statistics Explained article on use of artificial intelligence in enterprises
- Thematic section on digital economy and society
- Database on digital economy and society
- Digitalisation in Europe – 2024 edition
Methodological notes
- EU enterprises: at least 10 employees and self-employed persons.
- Data comes from the 2024 EU survey on ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises and refers to all enterprises with at least 10 employees or self-employed persons (classified in statistical classification of economic activities in the European Community (NACE) Rev. 2 sections C to J, L to N and group 95.1).
- Enterprises using Artificial intelligence refer to the following AI technologies:
- technologies performing analysis of written language (text mining)
- technologies converting spoken language into machine-readable format (speech recognition)
- technologies generating written or spoken language (natural language generation)
- technologies identifying objects or persons based on images (image recognition, image processing)
- machine learning (e.g. deep learning) for data analysis
- technologies automating different workflows or assisting in decision making (Al-based software robotic process automation)
- technologies enabling physical movement of machines via autonomous decisions based on observation of surroundings (autonomous robots, self-driving vehicles, autonomous drones)
- Machine learning (e.g. deep learning) involves ‘training’ a computer model to better perform an automated task, e.g. pattern recognition.
- Natural language processing, natural language generation or speech recognition are the ability for a computer program to understand human language as it is spoken, to convert data into natural language representation or to identify words and phrases in spoken language and convert them to a machine-readable format.
- France and Sweden: break in the time series in 2023.
Source – Eurostat

